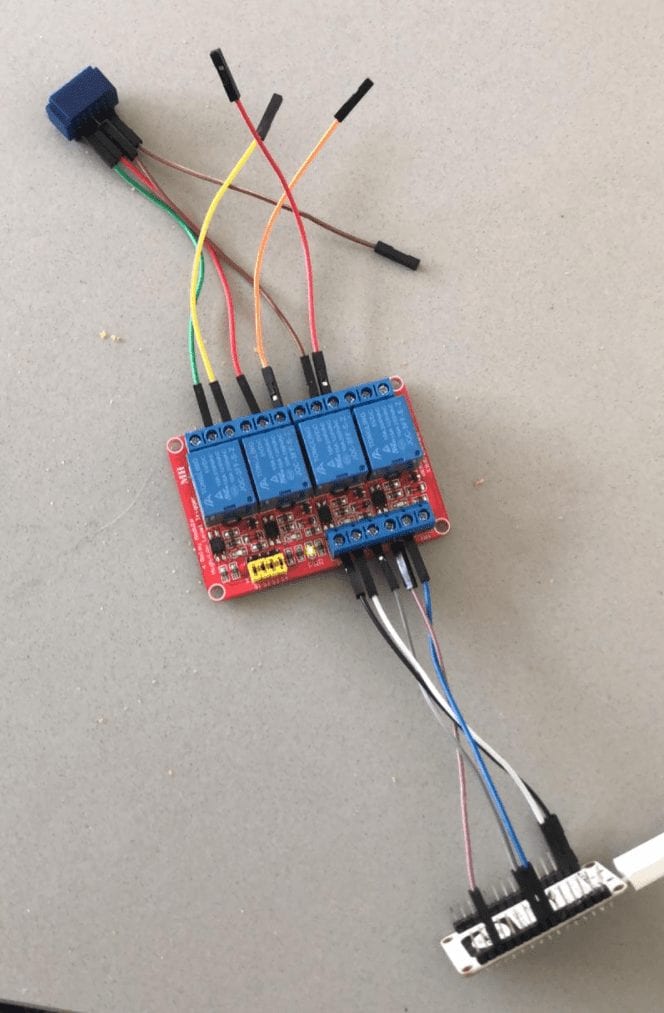
This article is part of the Make your Bellfire fireplace smart project that I presented during the Home Assistant Conference 2020.
We now have all ingredients for our solution, covered in the in the previous articles in this series. Before we start building, let’s take a look at how this all will work together end-to-end.
- Home Assistant, as home automation platform and for user interactions and automation
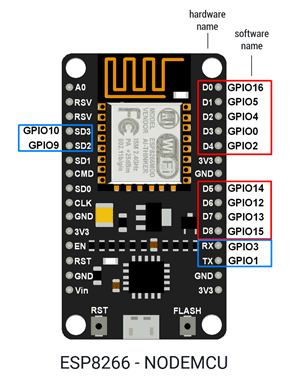
- ESP chip low cost connected controller hardware, providing GPIO pins to control the relay and WiFi connectivity
- ESPHome software that run’s on the ESP, providing the ability to configure actions with the relay and communication with Home Assistant.
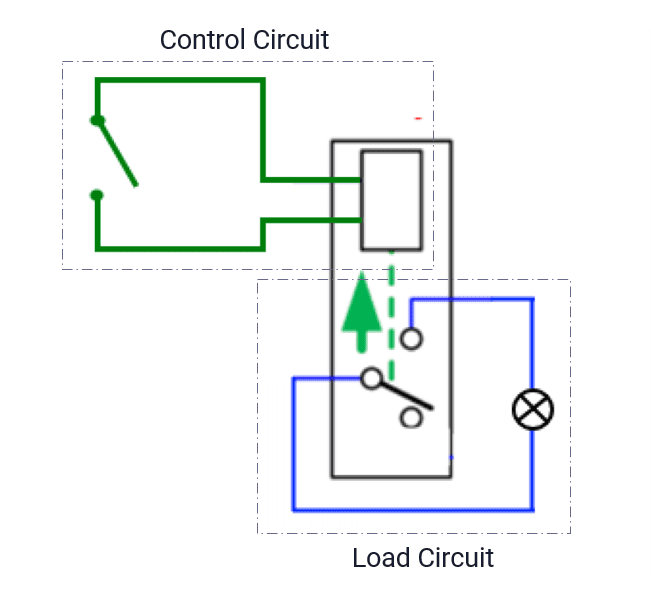
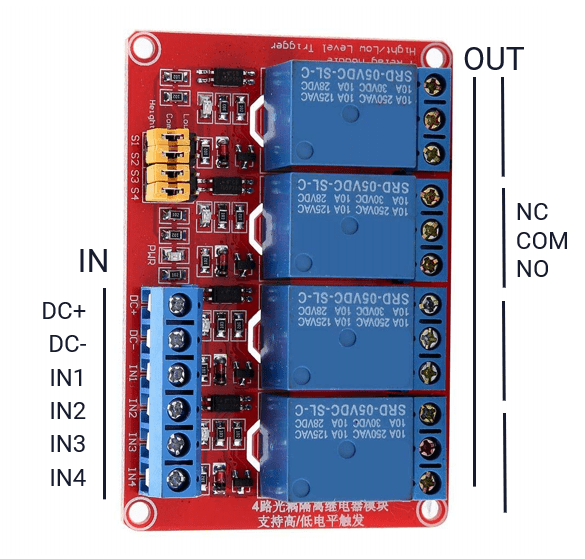
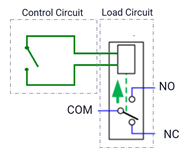
- Relay board with multiple relays that can control switches providing high or low power as input
In six simple steps we’ll make the fireplace smart.
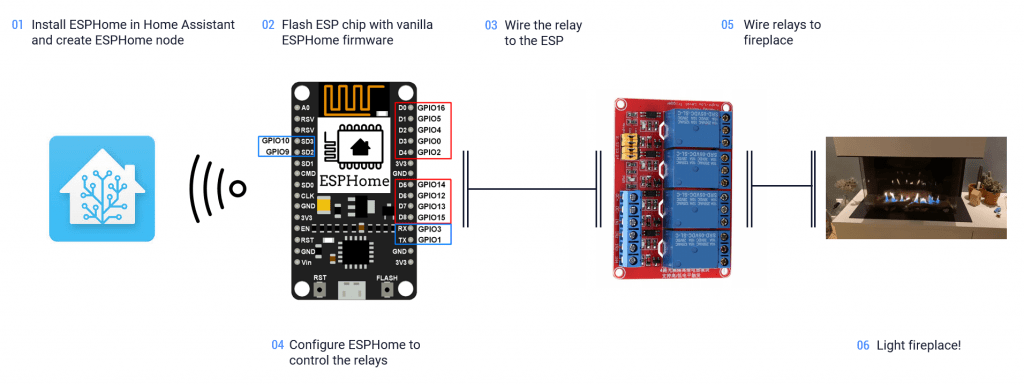
- Install ESPHome in Home Assistant and create ESPHome node
- Flash ESP chip with vanilla ESPHome firmware
- Wire the relay to the ESP
- Configure ESPHome to control the relays
- Wire relays to fireplace
- Light fireplace!
That’s it, let’s go and start building this out! The next article will cover installing ESPHome in Home Assistant and reating your first ESPhome node.